Describe in Words the Structure of a Typical Virus
However bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria have a unique shape with a geometric head and filamentous tail fibers. Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause a variety of diseases in humans and animals.

Virus Definition Structure Classification Examples Biology Dictionary
Viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements most probably of cellularorigin and characterized by a long co-evolution of virus and host.

. The nucleic acid encodes the genetic information which is unique for each virus. Describe the replication process of animal viruses. Human coronaviruses were.
What a virus is. The virion capsid has three functions. Be sure to discuss the following.
The typical structure of a virion which is the term used to describe a single virus includes an outer shell that is otherwise referred to as the protein capsid or membrane. This is a higher order of magnitude than an epidemic. The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell.
RNA viruses have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase that permits the usual sequence of DNA-to-RNA to be reversed so that the virus can make a DNA version of itself. Coronavirus any virus belonging to the family Coronaviridae. All viruses contain nucleic acid either DNA or RNA but not both and a protein coat which encases the nucleic acid.
Writing an academic essay means fashioning a coherent set of ideas into an argument. Here is a photo of the Influenza virus. Each virus possesses a protein capsid to protect its nucleic acid genome from the harsh environment.
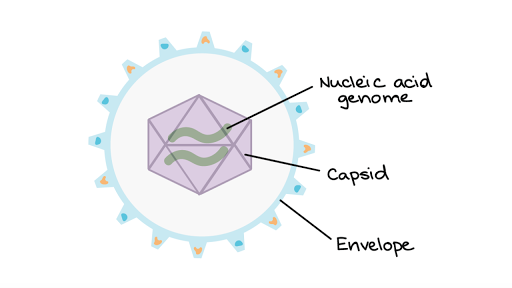
Some scientists speculate that viruses started as rogue segments of genetic code that adapted to a parasitic existence. A virus particle is made up of genetic material housed inside a protein shell or capsid. Describe the structure of a typical virus.
The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell. Because essays are essentially linearthey offer one idea at a timethey must present their ideas in the order that makes most sense to a reader. Researchers have grouped viruses together into several major families based on their.
Viruses infect all life forms from animals and plants to microorganisms including bacteria and archaea. As viruses are obligate intracellular pathogens they cannot replicate without the machinery and metabolism of a host cell. Objective 10 A virus consists of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protective coat.
RNA viruses include HIV and hepatitis C virus. The genetic material or genome of a virus may consist of single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA and may be linear or circular in form. They are also very versatile organisms surviving in extremely inhospitable conditions.
Virus capsids predominantly come in two shapes. Helices is a spiral shape that curves cylindrically around an axis. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website.
Hence they are classified as prokaryotic organisms. Coronaviruses have enveloped virions virus particles that measure approximately 120 nm 1 nm 10 9 metre in diameter. Unlike the growth curve for a bacterial population the growth curve for a virus population over its life cycle does not follow a sigmoidal curve.
Viral proteins on the capsid or phospholipid envelope interact with. The capsid shape varies from simple helical and icosahedra forms to more complex structures with tails. STRUCTURE OF A VIRUS Viruses contain nucleic acideither DNA deoxyribonucleic acid or RNA ribonucleic acid and protein.
Successfully structuring an essay means attending to a readers logic. Although the replicative life cycle of viruses differs greatly between species and category of virus there are six basic stages that are essential for viral replication. A typical virus consists of a protective protein coat known as a capsid.
Herpes simplex virus and the hepatitis B virus are DNA viruses. In other words think of outbreak as the building block of several other coronavirus-related terms. Some viruses are also enclosed by an envelope of fat and protein molecules.
Since Dmitri Ivanovskys 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck. What is the structure and genome of a typical plant virus. The structure of bacteria is known for its simple body design.
Club-shaped glycoprotein spikes in the envelope give the viruses a. Viruses generally come in two forms. 4 nucleic acid core protein coat or capsid envelope viralviral--specific enzymesspecific enzymes.
Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites which by definition containeither a RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective virus-coded protein coat. Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms with the absence of the nucleus and other c ell organelles. No matter the shape all viruses consist of genetic material DNA or RNA and have an outer protein shell known as a capsid.
A pandemic is a worldwide spread of a disease. The two most common causative agents of infectious disease are the virus and bacteriumBoth of these pathogens are invisible to the naked eye allowing for their stealthy transfer from person to person during an outbreak of a contagious diseaseWhile they rightly share a nasty reputation as disease agents their properties apart from the harm they cause are quite dissimilar. During the initial stage an inoculum of virus causes infection.
Theyre named for the distinctive crown-like spikes on the virus surface. A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. The infectious external covering core of a virus is called the virion.
Intro To Viruses Article Viruses Khan Academy

Virus Definition Structure Classification Examples Biology Dictionary
No comments for "Describe in Words the Structure of a Typical Virus"
Post a Comment